You’re here to unravel the buzzwords: Web1, Web2 and Web 3. Trust me, it’s like a trilogy, and each part is more exciting than the last.
But why should you care?
Because understanding this evolution is like holding a roadmap to the digital universe.
Plus, it could be a game-changer for your career and daily life. So, let’s get you geared up for the future!
Key Takeaways
Evolution Stages: The Internet has evolved from Web 1.0 (static and informational) to Web 2.0 (social and interactive), and now to Web 3.0 (decentralized and blockchain-based).
Web1.0: Characterized by static websites and limited user interaction, resembling a digital library.
Web2.0: Marked a shift to dynamic and interactive websites, emphasizing user-generated content and the rise of social media platforms.
Web3.0: Focuses on a decentralized web structure, leveraging blockchain technology, smart contracts, and virtual assets for enhanced user control and secure transactions.
Future Speculations (Web4.0): Anticipated to integrate artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing for a more personalized web experience.
Ethical Considerations: Raises questions about data ownership, privacy, and AI ethics in the context of an increasingly decentralized web.
Economic and Social Impact: Each web version has significantly influenced our economy and the way we interact socially.
The Dawn of Time: Web1.0
What Was Web1.0?
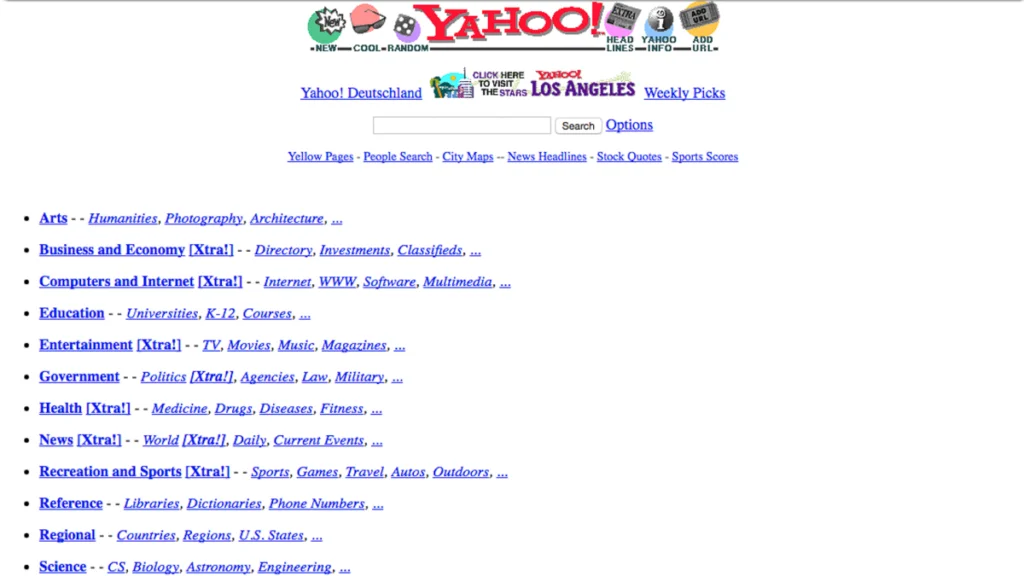
Web1.0 marked the early days of the internet, often referred to as the ‘read-only web’. It was a period of static websites with limited user interaction.
Web users could access a wealth of information, much like visiting a digital library, but their role was passive.
They were mere spectators in a world of unique web addresses and static pages, where content was delivered from a single server to the user’s browser.
Key Features of Web1.0
Static HTML Pages: Simple text and images marked the extent of Web1.0’s capabilities.
Limited User Interaction: Interaction was predominantly one-directional, from the web to the user.
Information Overload: The Web1.0 era was marked by an abundance of information, but lacking dynamic content and user engagement.
Real-World Example: The Encyclopedia
Remember those bulky encyclopedias? Web1.0 was like a digital version of that.
You’d go to a website, find what you need, and that’s it—end of interaction.
The Teenage Years: Web2.0
What is Web2.0?
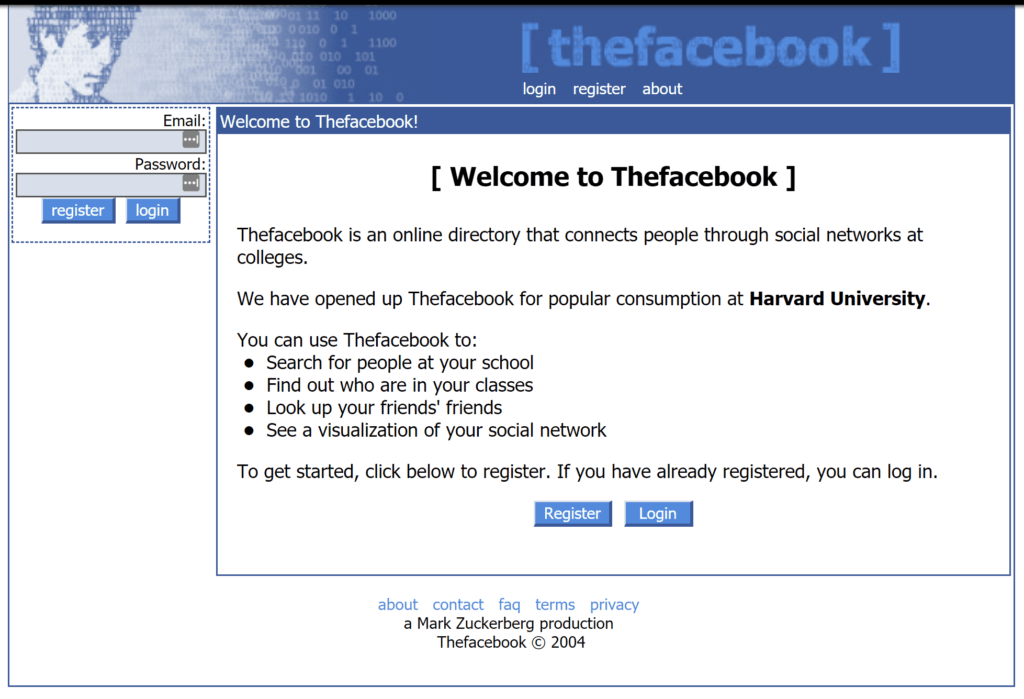
Transitioning to Web2.0, the internet’s evolution took a significant leap. This period, often synonymous with the ‘social web’, introduced dynamic and interactive websites.
Web2.0 was not just about reading content; it was about creating it. This era saw the rise of social media platforms and blogs, enabling users to become content creators.
Plus, it paved the way for the gig economy, think Uber and Airbnb.
Key Features of Web2.0
Social Media: The emergence of platforms like Facebook revolutionized how we connect.
User-Generated Content: From blogs to videos, users were no longer just consumers but also creators.
Interactive Websites: Sites became more dynamic, offering interactive experiences.
Real-World Example: Wikipedia vs Encyclopedia
Wikipedia is the epitome of Web2.0.
The Future is Now: Web3.0
What is Web3.0?
Web3 represents the current version and the future of the internet.
It’s a decentralized web, marked by decentralized protocols and blockchain technology.
This era of e commerce is defined by user control and secure transactions, leveraging technologies like smart contracts to create a more user-centric web.
What’s behind decentralization and blockchain technology, you ask?
Imagine a network run by its users, not by central authority or a single corporation.
It’s the realm of cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and smart contracts.

Key Features of Web3.0
Decentralization: This key characteristic of Web3.0 removes central authority, enabling users greater control.
Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts written into code, enhancing trust and security in online transactions.
Virtual Assets: The rise of NFTs and cryptocurrencies has redefined asset ownership on the web.
Real-World Example: Decentraland vs Facebook
Ever wanted to own virtual land? In Decentraland, a decentralized Web3 platform, you can.
Unlike Facebook where you can “own” a page, in Decentraland you can actually own, sell, and trade virtual properties using cryptocurrency.
Web1 vs Web2 vs Web3: The Showdown
Each version of the web brought with it distinct advantages and challenges.
From the static, information-heavy Web1.0 to the social and interactive Web2.0, and now to the decentralized and blockchain-based Web3.0.
The internet’s evolution has been marked by a steady shift towards greater user engagement and control.
| Feature | Web1.0 | Web2.0 | Web3.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interactivity | Limited | High | Ultra-High |
| Control | Centralized | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Main Focus | Information | Interaction | Transactions |
| User Role | Spectator | Participant | Owner |
| Data Storage | Server-based | Server-based | Blockchain |
| Financial Transactions | Basic E-commerce | Advanced E-commerce | Crypto-based |
| Identity | Anonymous | Social Media Profiles | Blockchain IDs |
| Content Creation | Webmasters | Anyone | Anyone |
| Search Capability | Basic | SEO Optimized | Semantic Search |
| Connectivity | Hyperlinks | APIs | Smart Contracts |
| Speed | Slow | Faster | Fastest |
| Security | Basic | Improved | Strongest |
| Collaboration | None | Social Sharing | Decentralized Collaboration |
| Customization | None | User Preferences | AI-driven |
| Accessibility | Desktop | Mobile-friendly | Any Device |
| Monetization | Ad-based | Ad-based & Subscription | Token-based |
| Community Building | Forums | Social Media | DAOs |
| Privacy | Low | Medium | High |
| Ethical Considerations | Limited | Moderate | Complex |
| User Experience | Clunky | User-Friendly | Seamless |
What Could Web4.0 Look Like?
The Internet’s Enlightenment Era
Speculations about Web4.0 involve an even more integrated, intelligent, and intuitive web.
It could see the fusion of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to deliver highly personalized and relevant results.
The semantic web, a term closely related to this future version, implies a web that understands and interprets user data at a sophisticated level, offering an unparalleled user experience.
Key Features of a Hypothetical Web4.0
Hyper-Personalization: Your browser might know what you need before you do.
AI Integration: Virtual assistants could anticipate your questions.
Immersive Reality: Virtual and augmented reality could become as common as smartphones.
Ethical Considerations
As we progress through these phases of the web, ethical considerations, especially around data ownership, privacy, and AI ethics, become increasingly significant.
The decentralized structure of Web3.0 and beyond raises questions about data sovereignty and the responsibilities of decentralized platforms and networks.
AI Ethics: As artificial intelligence becomes more integrated, questions about decision-making, bias, and control will become more pressing.
Data Sovereignty: With data becoming more interconnected, who owns this data, and who gets to control it?
Human Augmentation: If Web4.0 includes bio-integration, this could raise ethical questions about accessibility and the potential for “superhumans.”
Real-World Example: Minority Report Revisited
In the movie Minority Report, predictive policing raises ethical questions about free will and privacy. If Web4.0 includes similar predictive technologies, we’ll need to address these ethical dilemmas head-on.
Wrapping Up the Ethical Angle
As we move from one version of information sharing the semantic web to another, the ethical considerations become more complex and far-reaching.
From basic concerns about data ownership and privacy in to potential bioethical debates in Web4.0, each phase presents its own set of challenges.
Understanding these ethical dimensions of online transactions is crucial for responsible participation in the digital world.
So, the next time you marvel at the latest web technology, take a moment to ponder the ethical implications.
After all, the world wide web itself doesn’t just evolve technologically; it evolves ethically too.
How to Transition from Web2.0 to Web3.0
Embracing Web3.0 involves understanding its core elements like blockchain technology and decentralized applications (dApps).
Users interested in this transition should educate themselves about these technologies and consider their implications for privacy, security, and digital identities.
Ready to make the leap? Here’s how:
Educate Yourself: Understand the basics of blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
Choose a Wallet: Pick a crypto wallet to store your digital assets.
Explore dApps: Dive into the world of decentralized apps.
Join a Community: Get involved in DAOs or NFT communities to truly experience the power of Web3.
Read more: A Complete Guide to Transitioning from Web2.0 to Web3.0
The Economic & Social Impact of Web Evolution
Each version of the web has had a profound impact on our economy. Web1 and web 1.0 that brought information to our fingertips, Web2.0 gave rise to the gig economy, and Web3.0 is setting the stage for a decentralized financial revolution through the key difference of a decentralized internet.
The Social Impact of Web Versions
From Web1.0 forums to Web2.0 social media sites and now to Web3.0 DAOs, each version of the web has redefined how we interact, build communities, and even tackle social issues.
Wrapping it Up
So there you have it, the evolution of the Internet in a nutshell. From a static library in Web1.0 to a bustling social hub in Web2.0, and now to a decentralized universe in Web3.0 with greater control.
And who knows what Web4.0 will bring?
The Internet is not just growing; it’s evolving, and you’re part of that journey of endless possibilities.
F.A.Q
What is Web1.0?
Web1.0 is the early phase of the Internet, focused on providing static information.
How is Web2.0 different from Web1.0?
Web2.0 is interactive and social, unlike the static and information-heavy Web1.0.
What makes Web3.0 the future?
Web3.0 is decentralized and enables direct peer-to-peer transactions.
Is Web3.0 only about cryptocurrencies?
No, Web3.0 encompasses NFTs, smart contracts, and much more.
How can I get involved in Web3.0?
Start by understanding cryptocurrencies and consider investing in or using decentralized apps (dApps).
Is Web2.0 obsolete?
No, Web2.0 platforms like social media are still very much active but are gradually integrating Web3 features.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code.
What are NFTs?
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, are unique digital assets verified using blockchain technology.
Is Web3.0 safe?
Web3.0 offers enhanced security through blockchain, but it’s essential to take personal security measures.
What are the drawbacks of Web3.0?
While Web3.0 offers many advantages, it’s still a developing space with challenges like energy consumption and regulatory uncertainty.







